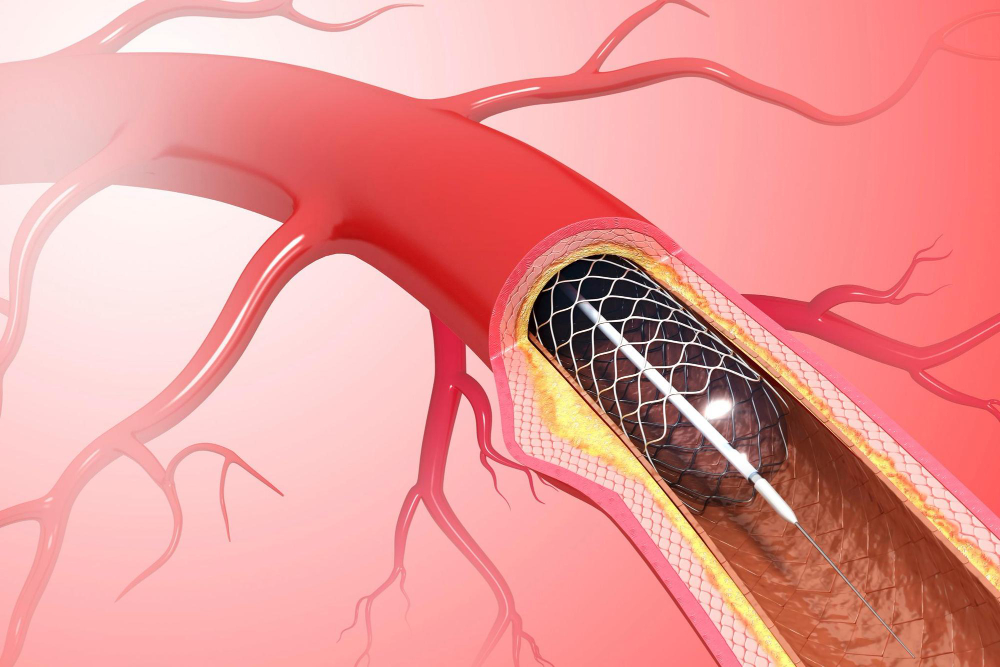
What Is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is a medical procedure that helps open blocked arteries. Doctors use it to improve blood flow to the heart. This treatment is also called a minimally invasive heart procedure. During angioplasty, a thin tube is used to widen narrowed or blocked blood vessels. These vessels carry blood to your heart. Many people know this as a common blocked arteries treatment. Angioplasty can help reduce chest pain and lower the risk of a heart attack.
Why Is Angioplasty Needed?
Sometimes, fatty deposits build up inside your arteries. This buildup is called plaque. Over time, plaque can block blood flow. When this happens, your heart does not get enough oxygen. As a result, you may feel chest pain or shortness of breath. In some cases, a blocked artery can cause a heart attack. Angioplasty is needed when:
According to the American Heart Association, angioplasty is a common way to treat heart disease. It can help many people live healthier lives.
How Is Angioplasty Performed?
Doctors perform angioplasty in a hospital. The procedure is safe and usually takes about one to two hours. Here is a simple step-by-step overview:
Because angioplasty is minimally invasive, recovery is often quick. Many people go home the next day.
Benefits and Risks of Angioplasty
Angioplasty offers many benefits. However, like all medical procedures, it also has some risks. Let’s look at both:
Most people have a safe experience. Still, it is important to talk with your doctor about your risks and benefits.
Recovery and Aftercare Tips
After angioplasty, you will need some time to heal. Your doctor will give you instructions to help you recover. Here are some helpful tips:
With proper care, most people return to normal activities within a week. However, always follow your doctor’s advice for the best results.
Prevention: Keeping Arteries Healthy
Even after angioplasty, it is important to keep your arteries healthy. This helps prevent future blockages. You can protect your heart by:
According to the World Health Organization, these healthy habits lower your risk of heart disease. They also help you feel better every day.
In summary, angioplasty is a safe and effective way to open blocked arteries. It can improve your heart health and quality of life. For more information, consult a heart specialist for personalized advice on angioplasty and heart health.